Introduction
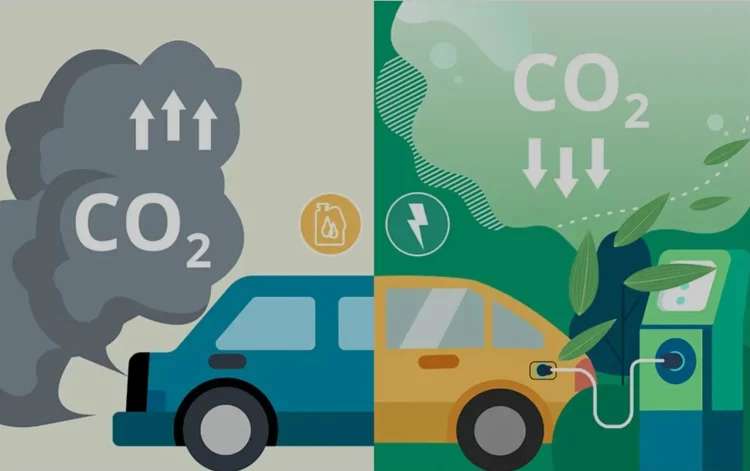
In the battle against climate change, cities are on the front lines. They are home to more than half of the world’s population and are responsible for a substantial portion of global carbon emissions. Transportation, particularly road transport, is one of the largest contributors to urban carbon footprints. The rise of electric vehicles (EVs) presents a transformative opportunity to reduce these emissions and reshape how cities approach sustainable mobility.
Electric vehicles, powered by clean electricity, have the potential to drastically cut down carbon emissions compared to their internal combustion engine (ICE) counterparts. In urban environments, where traffic congestion, poor air quality, and high levels of vehicle emissions are significant concerns, EVs can be a game-changer. This article explores how EVs can reduce urban carbon emissions, the factors driving their adoption, the challenges involved, and how cities around the world can leverage this technology to meet climate goals.
Section 1: The Problem of Urban Carbon Emissions
- Understanding Urban Carbon Footprints
- Overview of global urban carbon emissions, with a focus on transportation’s contribution.
- Impact of vehicle emissions on air quality, public health, and the environment.
- The urgency of addressing transportation-related emissions in cities.
- The Role of Internal Combustion Engine (ICE) Vehicles in Emissions
- How conventional vehicles powered by fossil fuels contribute to carbon emissions in cities.
- The relationship between population density, car ownership, and transportation emissions.
- Case studies of cities with high carbon footprints due to reliance on ICE vehicles.
- Health and Environmental Impacts
- Short- and long-term health effects of urban air pollution (e.g., respiratory diseases, cardiovascular issues).
- Environmental consequences of high levels of CO2, including climate change and rising urban temperatures.
Section 2: The Rise of Electric Vehicles and Their Environmental Benefits
- What Makes Electric Vehicles (EVs) Different?
- Explanation of how electric vehicles work compared to traditional gasoline or diesel cars.
- Benefits of EVs: zero tailpipe emissions, high energy efficiency, and lower operating costs.
- How EVs Reduce Carbon Emissions in Cities
- The direct impact of EVs on urban carbon emissions: comparison of emissions from EVs vs. ICE vehicles.
- The role of energy sources: how the environmental benefits of EVs increase as the grid becomes cleaner (renewable energy integration).
- Lifecycle emissions: production, use, and disposal—how EVs reduce emissions across their entire lifespan.
- Energy Efficiency of Electric Vehicles
- Comparison of the energy efficiency of electric vehicles vs. gasoline-powered cars.
- Why EVs use less energy to travel the same distance and the implications for reducing overall energy consumption in cities.
- Reducing Noise Pollution
- The additional environmental benefit of EVs in urban areas: quieter streets and less noise pollution.
Section 3: Policy and Government Incentives for EV Adoption
- The Role of Government Policies in Reducing Urban Emissions
- Overview of policies that encourage the adoption of EVs: subsidies, tax incentives, and grants for EV buyers.
- Carbon pricing and emissions regulations for cities to encourage cleaner transportation.
- Implementation of low-emission zones (LEZ) and incentives for EV infrastructure (e.g., charging stations).
- Case Studies of Successful EV Adoption
- Analysis of cities with aggressive EV adoption policies: examples from Norway, Amsterdam, and California.
- The impact of electric public transport and shared mobility on reducing carbon emissions in urban areas.
- How urban areas are leading the transition to electric fleets, including electric buses and delivery vehicles.
- The Role of Charging Infrastructure in Supporting EV Adoption
- How investments in EV charging stations are key to the success of widespread EV adoption in cities.
- Case study of cities with efficient charging networks, including lessons learned and challenges faced.
Section 4: The Environmental Impact of Electric Vehicles on Urban Air Quality
- How EVs Contribute to Cleaner Air
- The reduction of pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter (PM) in urban areas.
- The relationship between cleaner air and improved public health outcomes.
- Potential reductions in urban smog and the broader climate benefits of transitioning to electric mobility.
- Long-Term Environmental Benefits
- How sustained EV adoption contributes to the global reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
- The synergy between EV adoption and renewable energy expansion in cities.
- Urban Green Spaces and Quality of Life
- The role of reducing vehicle emissions in creating healthier, more sustainable cities.
- How less pollution leads to better quality of life, green spaces, and more walkable cities.
Section 5: Challenges and Barriers to EV Adoption in Cities
- Infrastructure Challenges
- The need for significant investments in charging infrastructure: ensuring accessibility, convenience, and sufficient coverage.
- Challenges in integrating EVs into the existing energy grid, particularly during peak hours.
- Cost and Affordability
- The initial higher cost of EVs compared to traditional vehicles and the need for further cost reductions.
- Addressing the affordability gap in urban areas, especially in developing countries or lower-income regions.
- Public Perception and Consumer Behavior
- Overcoming misconceptions about EVs: range anxiety, performance concerns, and charging infrastructure availability.
- Educational campaigns and incentives to shift public attitudes toward EV adoption.
- The Transition for Traditional Automakers
- The challenge for traditional automakers to pivot from producing ICE vehicles to EVs.
- How legacy manufacturers are dealing with the transition to electric mobility, including the investment in new technologies and retooling factories.
Section 6: The Future of Electric Vehicles in Urban Sustainability
- The Role of Smart Cities in EV Integration
- How smart city initiatives can enhance the role of EVs in reducing urban carbon emissions.
- Integration of EVs with other sustainable transportation options, such as shared mobility, electric bikes, and autonomous vehicles.
- Electric Vehicle Fleets and Shared Mobility
- The potential of electric taxis, delivery vehicles, and shared mobility fleets in reducing emissions.
- Case studies of cities like London, New York, and Beijing incorporating electric vehicles into their public transport systems.
- The Role of Renewable Energy in Supporting EVs
- How combining renewable energy sources with EV adoption creates a closed-loop system that maximizes environmental benefits.
- The potential for solar-powered charging stations and green energy solutions in urban settings.
- Long-Term Projections for Urban Carbon Emission Reductions
- Future trends and estimates for how widespread EV adoption could impact urban carbon emissions.
- The role of innovation, including battery recycling, vehicle-to-grid technologies, and improved battery efficiency in making cities even more sustainable.
Section 7: Conclusion
The transition to electric vehicles is a key component in reducing urban carbon emissions. Cities are at the forefront of this change, offering a unique opportunity to make a significant environmental impact. While challenges remain—ranging from infrastructure development to consumer acceptance—the benefits of EVs in terms of reducing air pollution, cutting down greenhouse gas emissions, and improving quality of life are undeniable.
As governments, companies, and citizens work together to expand EV adoption and integrate clean energy solutions, the future of urban transportation looks brighter than ever. The widespread adoption of electric vehicles has the potential to transform cities into cleaner, healthier, and more sustainable places to live.