The global push for electric vehicles (EVs) has been fueled by the urgent need to combat climate change, reduce air pollution, and transition to a more sustainable future. Proponents argue that EVs are a key solution to the environmental challenges posed by traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. But can electric vehicles truly save the planet? This article explores the environmental impact of EVs, examining how they reduce greenhouse gas emissions, the role of renewable energy in enhancing their sustainability, and the lifecycle environmental impact from production to disposal.
How EVs Reduce Greenhouse Gas Emissions Compared to Traditional Vehicles
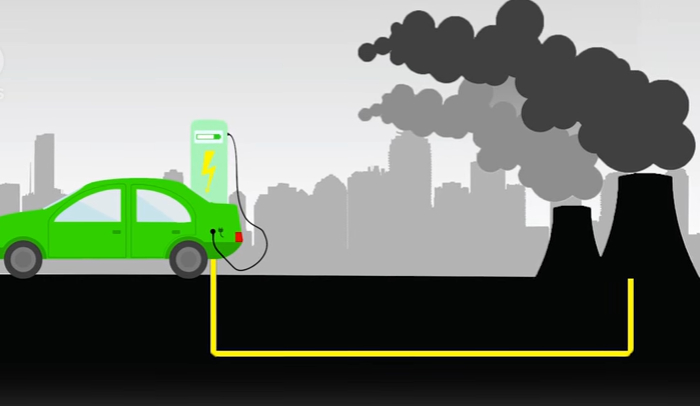
One of the most significant environmental benefits of electric vehicles is their potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Unlike ICE vehicles, which emit carbon dioxide (CO2) and other greenhouse gases directly from their tailpipes, EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions. However, the overall reduction in emissions depends on the source of the electricity used to charge the vehicles.
1. Zero Tailpipe Emissions
Electric vehicles operate on electric motors powered by rechargeable batteries, eliminating the need for gasoline or diesel. This fundamental difference means that EVs do not emit CO2, nitrogen oxides (NOx), or particulate matter (PM) during operation. In urban areas, where traffic congestion is a major source of pollution, the adoption of EVs can lead to significant improvements in air quality.
2. Lower Lifecycle Emissions
While EVs do not emit CO2 during operation, their overall environmental impact depends on the emissions associated with their production, charging, and disposal. Studies have shown that EVs generally have lower lifecycle emissions compared to ICE vehicles. This includes emissions from manufacturing, operation, and end-of-life disposal.
- Manufacturing Emissions: The production of EVs, particularly the batteries, involves energy-intensive processes that can generate significant emissions. However, advancements in manufacturing technology and the use of renewable energy in production facilities are helping to reduce these emissions.
- Operational Emissions: The emissions associated with charging EVs depend on the energy mix of the electricity grid. In regions where electricity is generated primarily from renewable sources, the carbon footprint of EVs is minimal. Even in regions with a higher reliance on fossil fuels, EVs tend to be more efficient than ICE vehicles, resulting in lower overall emissions.
- End-of-Life Emissions: The disposal and recycling of EV batteries can have environmental impacts, but advancements in battery recycling technology are helping to mitigate these effects. Recycling batteries can recover valuable materials such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, reducing the need for new mining and the associated environmental impacts.
3. Renewable Energy Integration
The environmental benefits of EVs are significantly enhanced when they are charged using electricity generated from renewable sources such as wind, solar, or hydroelectric power. In regions where the electricity grid is predominantly powered by renewables, EVs can achieve near-zero emissions over their lifetime.
- Grid Decarbonization: As power grids around the world transition to cleaner energy sources, the carbon emissions associated with EVs will continue to decrease. This makes EVs a more sustainable option in the long term, even in regions currently reliant on fossil fuels.
- Energy Storage: EVs can serve as mobile energy storage units, allowing for the storage of excess renewable energy generated during periods of low demand. This stored energy can then be used to power homes and businesses during peak demand periods, reducing the need for fossil fuel-based power plants and enhancing grid stability.
The Role of Renewable Energy in Enhancing EV Sustainability
The sustainability of electric vehicles is closely tied to the energy sources used to generate the electricity that powers them. Renewable energy plays a crucial role in maximizing the environmental benefits of EVs.
1. Reducing Carbon Footprint
When EVs are charged using electricity generated from renewable sources, their carbon footprint is significantly reduced. This is because renewable energy sources such as wind, solar, and hydroelectric power produce little to no greenhouse gas emissions during operation.
- Solar Power: Solar energy is one of the most widely available renewable energy sources. Installing solar panels at home or using solar-powered charging stations can further reduce the carbon footprint of EVs.
- Wind Power: Wind energy is another clean and abundant source of electricity. Wind farms can generate large amounts of electricity with minimal environmental impact, making them an ideal complement to EV charging infrastructure.
- Hydroelectric Power: Hydroelectric power, generated from flowing water, is a reliable and renewable energy source that can provide a steady supply of electricity for EV charging.
2. Enhancing Energy Independence
The integration of renewable energy with EVs can enhance energy independence by reducing reliance on imported fossil fuels. Many countries depend on oil imports to meet their energy needs, which can have geopolitical and economic implications. By transitioning to electric mobility and renewable energy, countries can reduce their dependence on foreign oil and invest in domestic energy sources.
3. Supporting Smart Grids
Renewable energy and EVs can work together to support the development of smart grids, which optimize energy use and enhance grid stability.
- Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) Technology: V2G technology allows EVs to interact with the power grid, enabling them to store and supply energy as needed. This can create new revenue streams for EV owners and enhance the stability and resilience of the energy system.
- Smart Charging: Smart charging solutions optimize the use of available energy resources, reducing the strain on the grid and maximizing the use of renewable energy. This includes dynamic pricing, time-of-use tariffs, and demand response programs.
Analyzing the Lifecycle Environmental Impact of EVs
To fully understand the environmental impact of electric vehicles, it is essential to consider their entire lifecycle, from production to disposal.
1. Production Phase
The production of EVs, particularly the batteries, involves energy-intensive processes that can generate significant emissions. However, advancements in manufacturing technology and the use of renewable energy in production facilities are helping to reduce these emissions.
- Battery Production: The production of lithium-ion batteries requires the extraction and processing of raw materials such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel. These processes can have environmental and social impacts, including habitat destruction, water pollution, and greenhouse gas emissions. Sustainable mining practices and the development of alternative materials are essential for reducing these impacts.
- Manufacturing Emissions: The assembly of EVs involves energy-intensive processes that can generate emissions. However, many automakers are investing in renewable energy and energy-efficient manufacturing practices to reduce their carbon footprint.
2. Operational Phase
The operational phase of EVs is where their environmental benefits are most pronounced. EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions and are more energy-efficient than ICE vehicles.
- Energy Efficiency: Electric motors are inherently more efficient than internal combustion engines, converting over 60% of the electrical energy from the grid into useful work. This higher efficiency translates to lower energy consumption and reduced environmental impact.
- Charging Emissions: The emissions associated with charging EVs depend on the energy mix of the electricity grid. In regions where electricity is generated primarily from renewable sources, the carbon footprint of EVs is minimal. Even in regions with a higher reliance on fossil fuels, EVs tend to be more efficient than ICE vehicles, resulting in lower overall emissions.
3. End-of-Life Phase
The disposal and recycling of EV batteries can have environmental impacts, but advancements in battery recycling technology are helping to mitigate these effects.
- Battery Recycling: Recycling EV batteries can recover valuable materials such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, reducing the need for new mining and the associated environmental impacts. Developing closed-loop recycling systems and second-life applications for used batteries can further enhance sustainability.
- Waste Management: Proper disposal of EV batteries is essential to prevent environmental contamination. Many automakers and battery manufacturers are implementing take-back programs to ensure that used batteries are recycled or disposed of responsibly.
Conclusion
Electric vehicles have the potential to significantly reduce greenhouse gas emissions, improve air quality, and promote sustainability. However, their environmental impact depends on several factors, including the source of the electricity used to charge them, the efficiency of their production processes, and the management of their end-of-life disposal. By integrating renewable energy, advancing battery technology, and implementing sustainable practices, the EV industry can maximize its environmental benefits and contribute to a cleaner, greener future. While challenges remain, the transition to electric mobility is a critical step in addressing the environmental challenges of our time.











































